Scaphoid Fracture
The scaphoid fracture is the most common fracture of the wrist joint. A scaphoid fracture involves a break in the carpal bone. This bone is located on the thumb side of the wrist. But what exactly is a scaphoid fracture, how does it occur, what are the symptoms, and how is a scaphoid fracture treated? We will explain all of this below.
What is a scaphoid?
The scaphoid is often referred to as the “boat-shaped bone.” When this bone breaks, it is called a scaphoid fracture. The hand and forearm are connected at the wrist by several carpal bones. Carpal bones are small bones that allow your wrist to move smoothly. The ‘os scaphoid’ (‘os scaphoideum’) is an important carpal bone located on the thumb side. The scaphoid is relatively easy to find. When the thumb moves outward, a triangular hollow appears between two tendons on the thumb side of the hand. This area is known as the anatomical snuffbox. The scaphoid lies beneath this anatomical snuffbox. If the hand or wrist is swollen, this anatomical snuffbox may be less visible.
A scaphoid fracture means that one of these small bones is broken. Healing typically takes time, and additional injury may occur. This increases the risk of avascular bone necrosis, a condition in which the bone tissue dies due to reduced blood supply.
How does a scaphoid fracture occur?
A scaphoid fracture often results from a fall onto an outstretched hand with an overextended wrist. People who engage in activities such as skating, snowboarding, inline skating, or other types of contact sports are at higher risk.
What are the symptoms of a scaphoid fracture?
These are the most common symptoms of a scaphoid fracture:
- Swelling in the wrist.
- Pain when moving the thumb.
- Reduced range of motion in the wrist.
- Pain on the thumb side of the hand/wrist.
- Pressure from the thumb can cause discomfort.

How is a scaphoid fracture treated?
There are two types of treatment for a scaphoid fracture: conservative and surgical.
Conservative
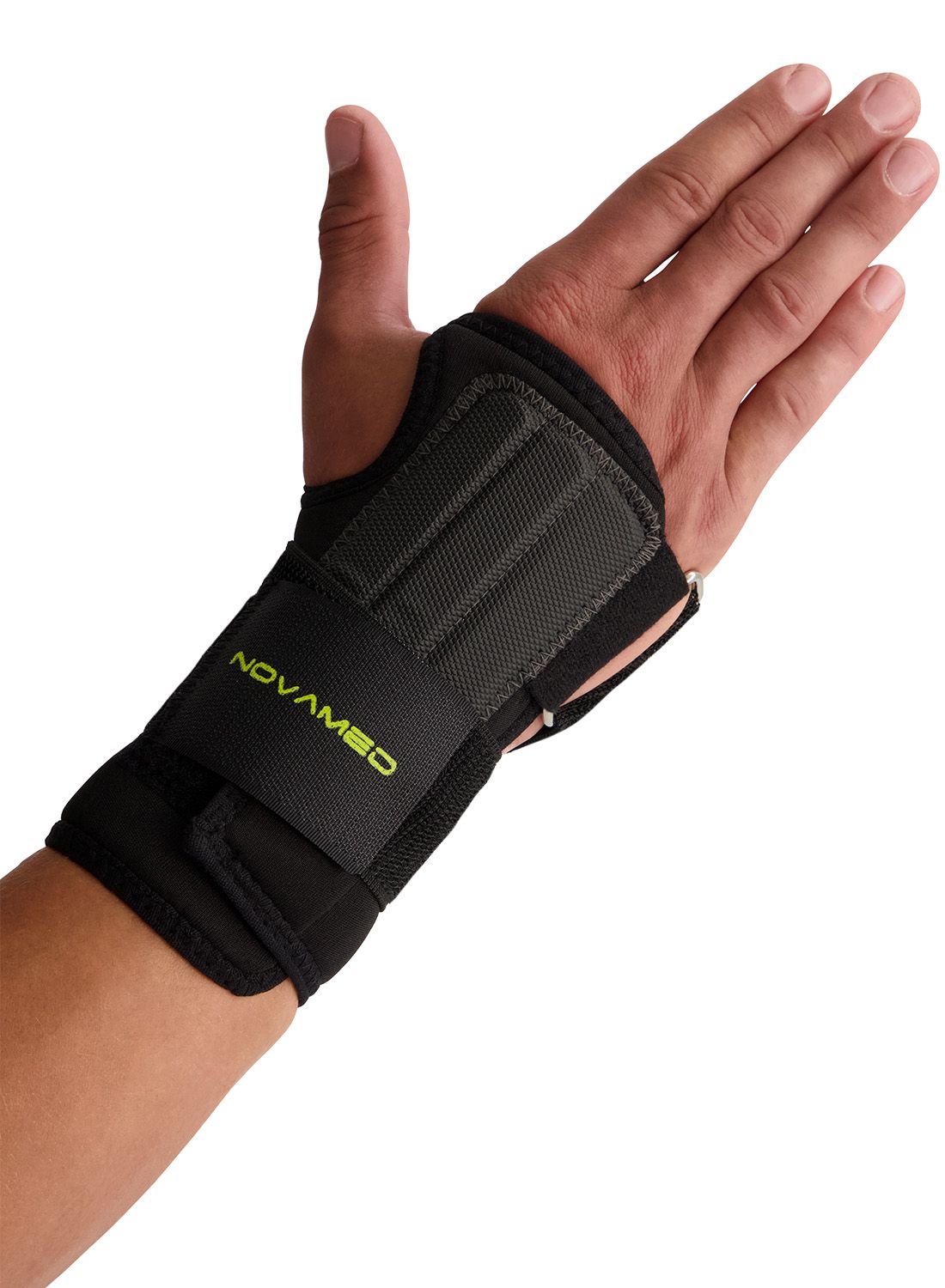
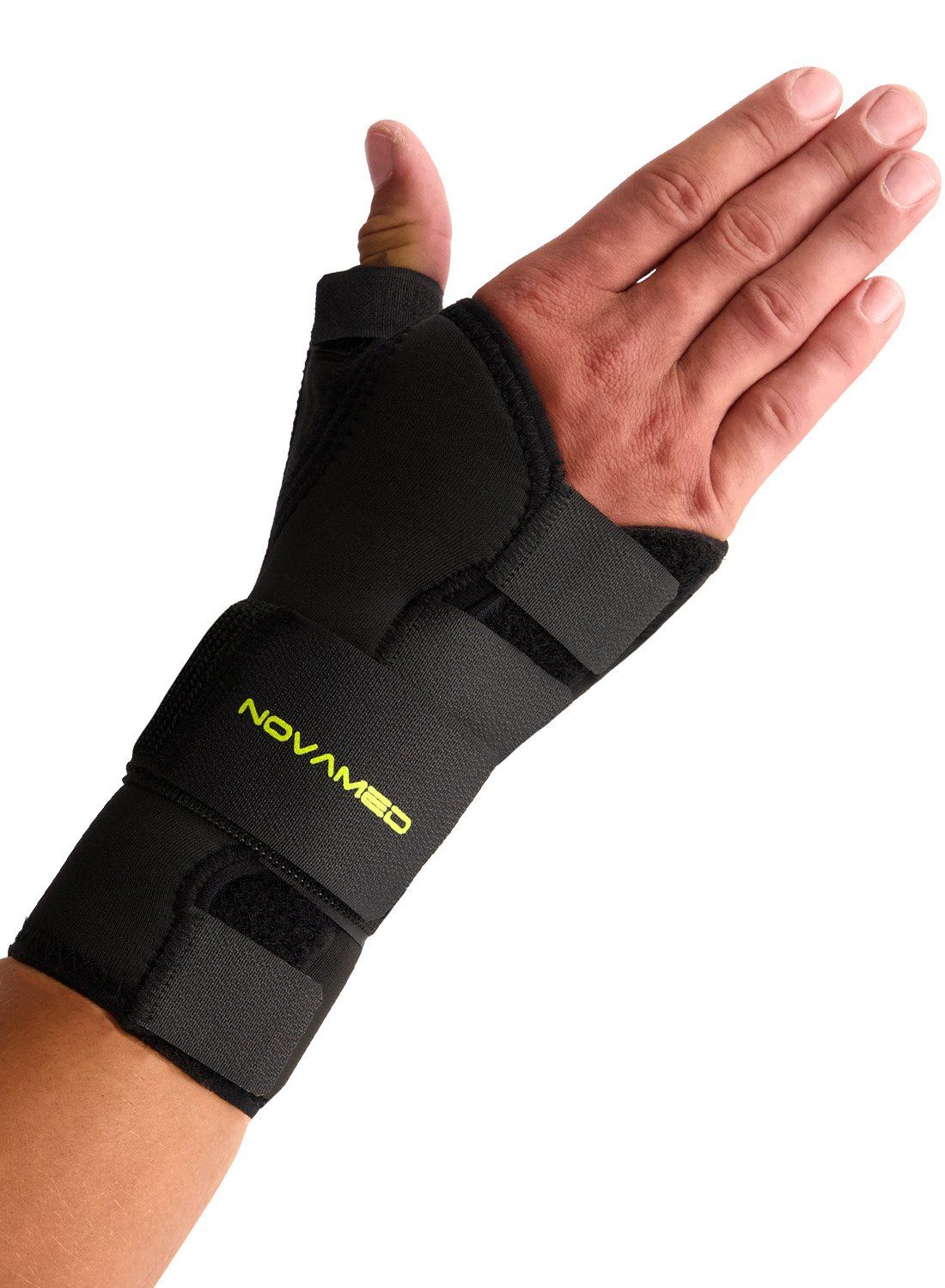
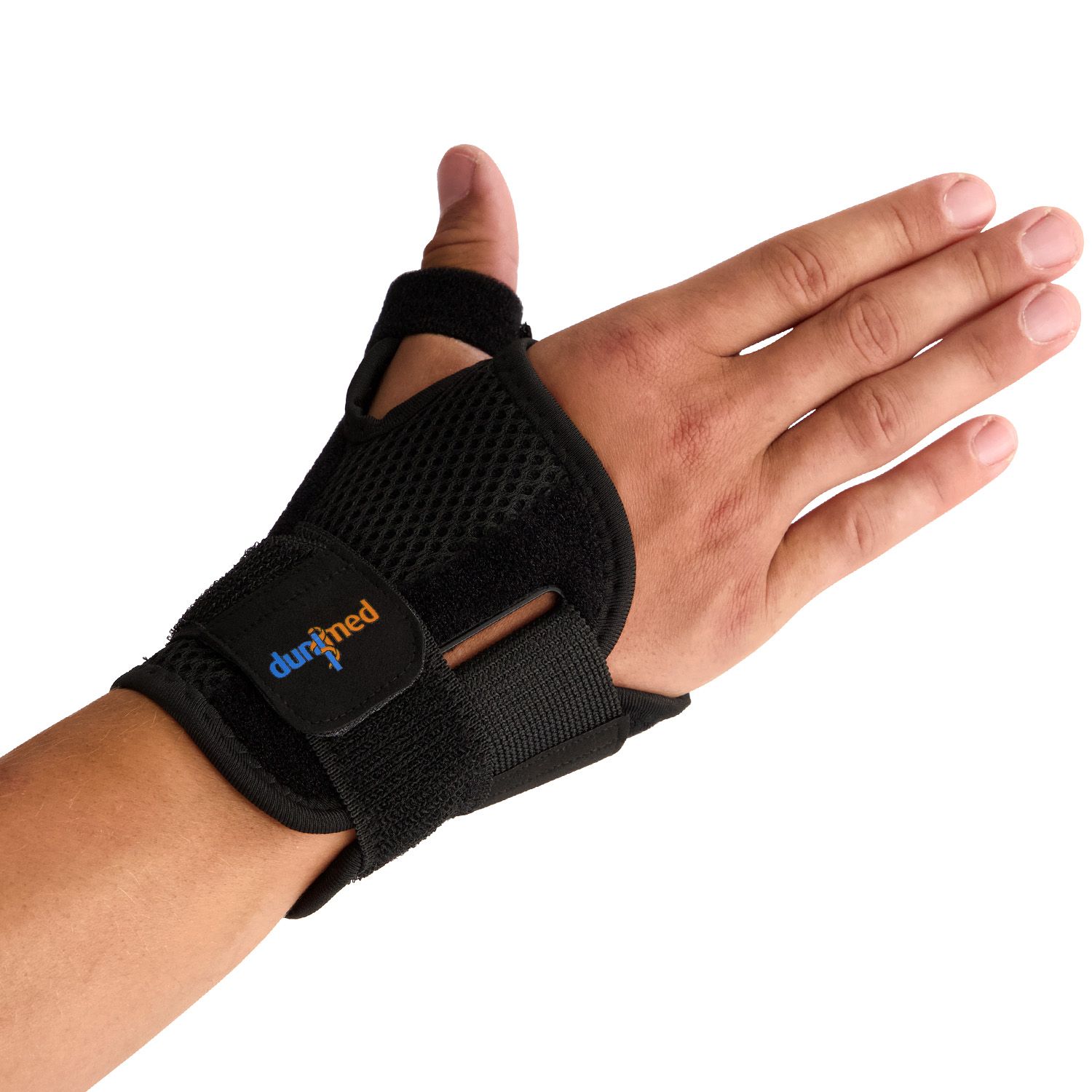
When the fracture is stable and has not shifted, it can be treated without surgery. In such cases, a (plaster) splint or a wrist brace is commonly used. The total recovery time can be up to 12 weeks. During the recovery period, X-rays are taken to monitor the healing process.
Surgical
Surgery is considered when conservative treatment has not been effective. Surgery may also be chosen if the fracture has shifted or healed improperly. After surgery, wearing a wrist brace is recommended, as the brace helps relieve stress on the wrist.

- Physiotherapist
- Sports podiatrist
- Manual therapist
- Podopostural therapist
- Myofascial dry needling specialist