Unstable wrist
An unstable wrist is caused by weakened or damaged ligaments between the wrist bones. This condition is also known as midcarpal instability. Below, we provide additional information about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Read on to learn more:
What is an unstable wrist?
The wrist consists of 8 small bones and 26 ligaments. These ligaments connect the wrist bones to each other. When you move your wrist, these ligaments move along with it. They also provide stability to the wrist. If these ligaments become weakened for any reason, the condition is referred to as wrist instability.
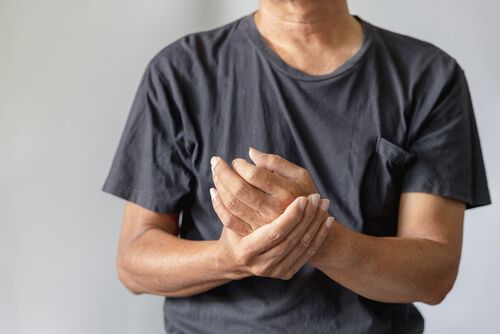
What causes an unstable wrist?
Wrist instability can be caused by damage to the bones, tendons, ligaments, or muscles. This may result from trauma to the wrist.
Overuse is also a possible cause. For example, if you play sports or take a hard fall and make a wrong movement, the ligaments can be injured. This can prevent the radius and ulna from being held together properly, leading to instability.
What are the symptoms?
If you have an unstable wrist, you may experience several symptoms. The most common one is pain, especially at the back (dorsal side) of the wrist. Loss of strength is another frequent symptom of wrist instability, which may cause you to drop objects.
You might also feel or hear a click when moving your wrist side to side, or get the sensation that your wrist is locking.
How is wrist instability diagnosed?
Wrist instability is diagnosed by a doctor, who may refer you to an orthopedic specialist. Usually, an X-ray is taken, which may already show signs of instability. However, this is not always the case.
In that situation, further testing may be done using a CT scan or an MRI scan.

What treatments are available to relieve wrist instability?
Treatment of wrist instability primarily involves physiotherapy. Your physiotherapist may choose from various methods, including:
- Manual therapy
- Exercise therapy
- Dry needling
- Taping
- Massage
You will also receive specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the wrist, which helps improve stability. If physiotherapy does not provide enough relief, surgery may be considered. The major drawback of surgery is that it often reduces wrist mobility, so this option is usually seen as a last resort. Whether you choose physiotherapy or surgery, wearing a wrist brace is highly recommended in both cases. A wrist brace provides optimal support and features a perfect fit, allowing full use of your fingers.

Super Ortho - Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Wrist Support

Super Ortho Wrist Support
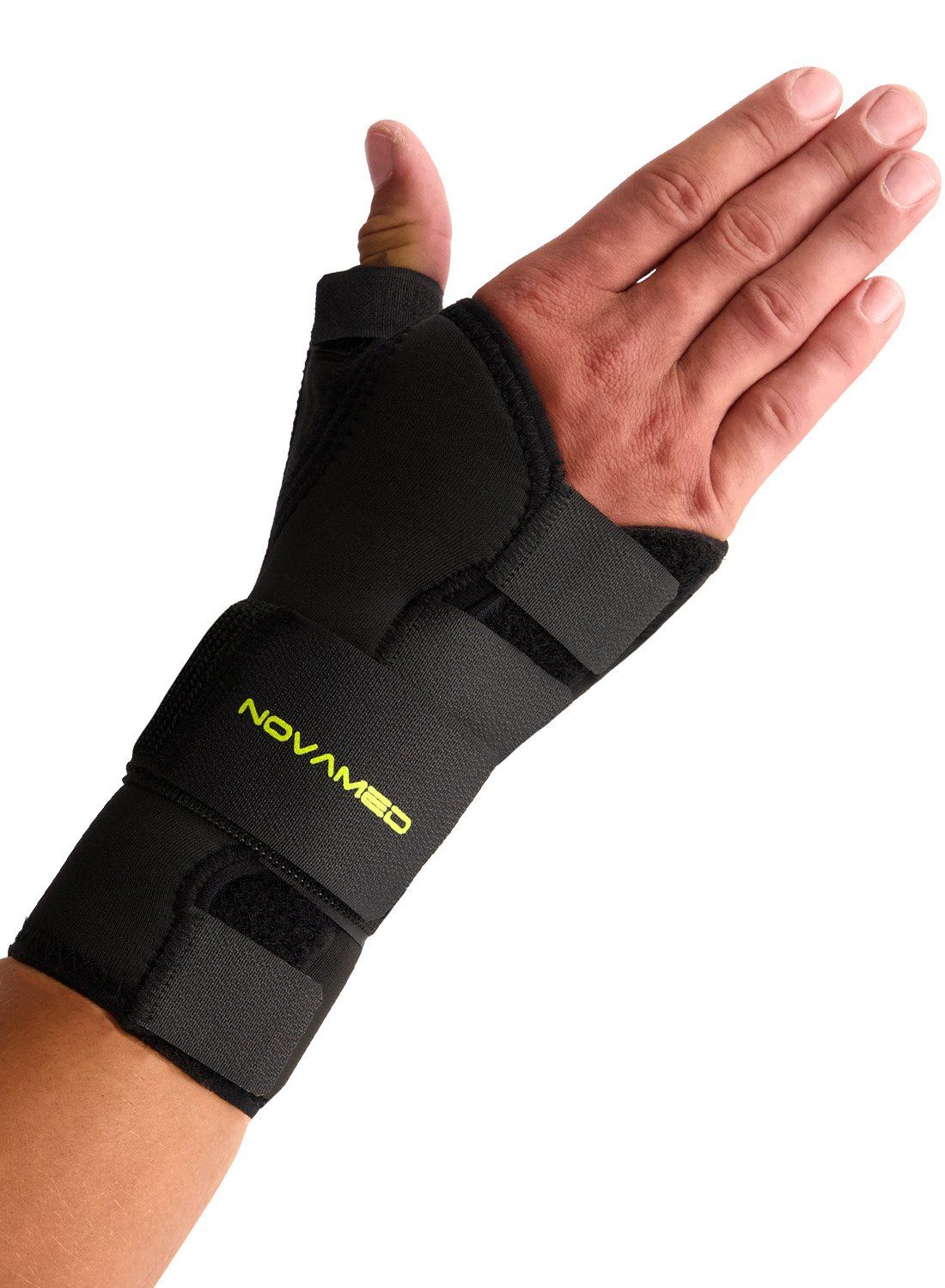

Novamed Thumb Support / Wrist Splint
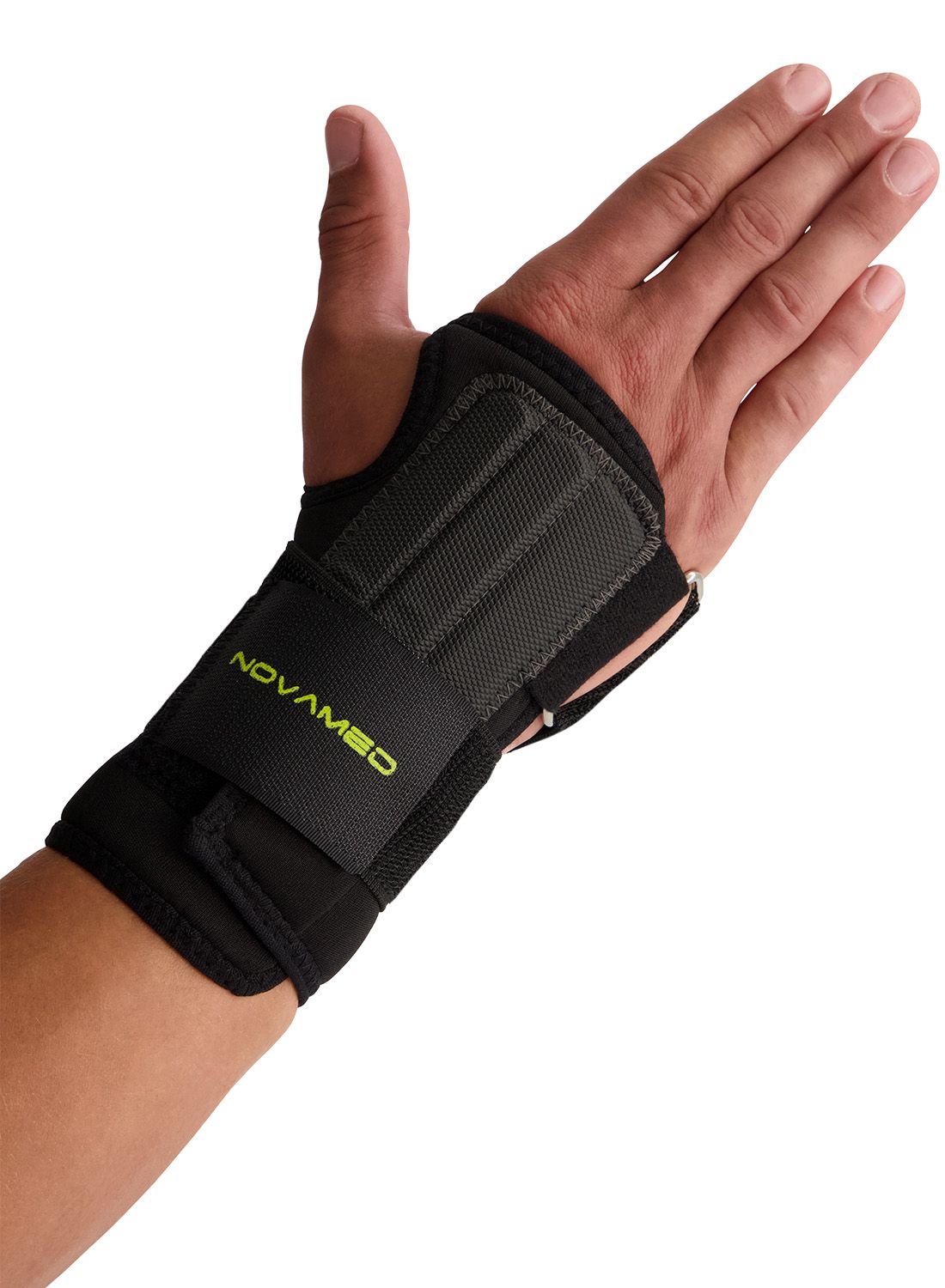

Novamed Lightweight Wrist Support
Dunimed Premium Thumb / Wrist Support
Dunimed Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Wrist Support

Dunimed Wrist Support

Dunimed Wrist Wrap

- Physiotherapist
- Sports podiatrist
- Manual therapist
- Podopostural therapist
- Myofascial dry needling specialist


